San Jose Scale Predictive Model
San Jose scale is an extremely important indirect pest of apples, pears, peaches, and plums. It is a sucking insect that injects a toxin into the plant as it feeds causing localized discolorations. Left uncontrolled, San Jose scale can damage fruit, kill limbs, or even kill the entire tree.
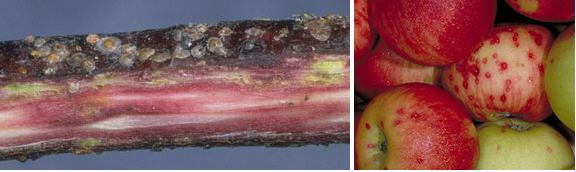
If such damage is noted, inspect trees for scale, especially one year-old wood. Purplish-red halos under the young bark are indications of scale infestation. Often this very small insect goes unnoticed until large populations have developed or fruit damage is observed.
San Jose scale overwinter as immature scales. In the spring, the tiny winged males emerge and mate with the wingless females. About one month after the male flight, the crawlers can be seen. Insecticides can either be used at the pink stage or timed to coincide with crawler emergence. Crawlers are the first minute stages that move around randomly on bark and foliage before settling down permanently. Timing of a spray is important as a few days after beginning to feed, a crawler secretes a waxy covering over its body that protect it from pesticides.

Minute crawlers stuck to black sticky tape.
Pheromone Trapping & Degree Day Accumulation
Pheromone trapping involves the use of chemical lures to attract male scales. A trap consists of a lure suspended between the two sticky sides of a tent-like trap. Pheromone traps for this insect should be placed in scale infested trees either prior to or during bloom. Male scales are extremely small gnat-like insects, so traps need to be examined carefully. Scales appear as a fine dust on the trap, usually concentrated on the sticky surface near the pheromone lure.
The date that the first males are caught in the trap is termed the biofix date. Male flight usually occurs after petal fall (mid to late April). Pheromone traps need to be examined daily in order to known when biofix occurs. After the biofix has occurred, degree days are calculated on a daily basis and are compared with the target values in the following table.